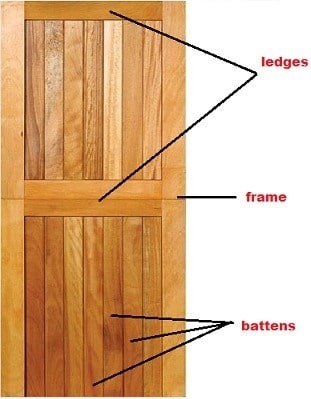
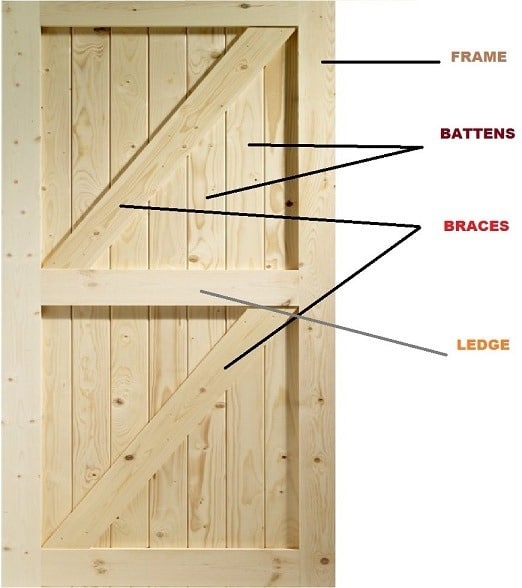
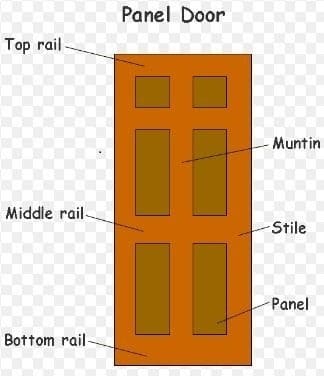
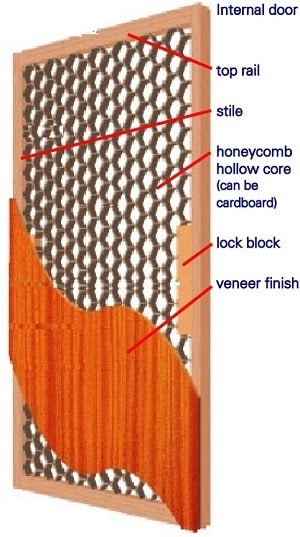
Hai welcome to our blog.
Let's see how to calculate material requirement for concrete.
For example we take M20 concrete.
M20 concrete
Where 20 is the compressive strength.
M- mix design. The mix ratio for M20 concrete is 1:2:4. 1stands for cement, 2 stands for fine aggregate, 4 stands for coarse aggregate. There is thumb rule for plain cement concrete and reinforced cement concrete that is the total volume of plain cement concrete is 1.52 cubic metre and for reinforced concrete the total volume of mixture is 1.57 cubic metre.
Plain cement concrete is laid by using 40 mm size blue metal in maximum cases. Reinforced cement concrete is laid by 20 mm size blue metal in maximum cases. The blue metals used for both concrete are free from dust and foreign substances.
Let's see the calculation for reinforced concrete m20
For M 20 concrete
The total volume of mixture is 1.57 cubic metre. The mix ratio of M20 concrete is 1:2:4 the sum of mix is 1+2+4 =7 . Let's see the calculation for cement, in mix ratio the term 1is cement so 1/7 ×1.57 = .0.22 cubic metre.
Where 1 is cement, 7 is the sum of mix ratio and 1.57 is volume of mixture for reinforced cement concrete.
For fine aggregate 2/7×1.57= 0.44 cubic metre.
For coarse aggregate 4/7×1.57 = 0.89 cubic metre.
Water should be river water for one cubic metre one thousand litre of water is used.
Therefore for M20 concrete the material requirement is
Cement - 0.22 cubic metre
Fine aggregate - 0.44 cubic metre
Coarse aggregate - 0.89 cubic metre
Water - 1000 litre
Thank you..